Pricing your products is one of the most crucial decisions for any business. The right pricing strategy can maximize profitability, attract customers, and help you stay competitive. On the other hand, the wrong pricing strategy can lead to lost sales or eroded profit margins. In this article, we’ll explore key strategies for pricing your products effectively and ensuring maximum profitability.
When setting prices for maximum profitability, it’s crucial to understand your customers’ entertainment preferences and spending habits. Many businesses overlook how leisure activities, such as enjoying Australian pokies games, influence disposable income allocation.
Aligning your pricing strategy with market trends ensures you capture value effectively. Consider how consumer behavior in gaming sectors reflects broader purchasing patterns.
Analyzing competitor pricing in similar entertainment niches can provide valuable insights. Implementing tiered pricing models often maximizes revenue across different customer segments.
Regularly reviewing your price points maintains competitiveness while protecting profit margins in dynamic markets.
1. Understand Your Costs
Know Your Break-Even Point
Before setting a price, it’s essential to understand all the costs associated with your product. This includes production costs, shipping, packaging, marketing, labor, and overheads. Knowing your break-even point—the minimum price you need to charge to cover your costs—will provide a foundation for setting your price.
Tip: Always factor in both fixed costs (e.g., rent, salaries) and variable costs (e.g., raw materials, shipping) when calculating the cost of your product.
2. Analyze the Market and Competitors
Conduct a Competitive Analysis
Researching competitors in your industry will give you a sense of the price range for similar products. Compare features, quality, and brand positioning to understand where your product fits within the market. If your product offers additional value, you may be able to price it higher than competitors. If it’s similar or less differentiated, a lower price might be more competitive.
Tip: Look at both direct and indirect competitors to get a full picture of market pricing.
3. Consider Your Target Audience
Price According to Customer Willingness to Pay
Your pricing should align with the expectations and buying power of your target audience. Conduct market research to determine how much your target customers are willing to pay for your product. Consider factors like age, income level, location, and buying behavior. For example, luxury goods tend to attract customers who are willing to pay a premium, while value-conscious customers may prioritize affordability.
Tip: Use customer surveys, focus groups, or social media polls to gauge willingness to pay.
4. Choose the Right Pricing Model
Select a Strategy That Fits Your Business Goals
There are various pricing strategies you can use, depending on your goals and market conditions:
- Cost-Plus Pricing: Add a fixed markup to the cost of production. This is a straightforward method that ensures you cover costs and make a profit.
- Penetration Pricing: Set a low price to attract customers and gain market share, then gradually increase the price once you have a loyal customer base.
- Skimming Pricing: Start with a high price and lower it over time. This works well for innovative or high-demand products.
- Value-Based Pricing: Set prices based on the perceived value of the product to the customer rather than the cost of production.
- Psychological Pricing: Use strategies like pricing items at $9.99 instead of $10 to make products appear less expensive.
Tip: Choose a pricing model that aligns with your brand positioning. Luxury brands often use skimming pricing, while mass-market products may use penetration pricing.

5. Factor in Psychological Pricing
Use Pricing Tactics to Influence Buying Decisions
Psychological pricing strategies can encourage customers to make a purchase. For example:
- Charm Pricing: Pricing products just below a whole number, like $19.99 instead of $20, makes the price seem more attractive.
- Bundling: Offer a deal where customers can buy multiple products together at a discount, encouraging them to spend more.
- Price Anchoring: Display the original price next to a discounted price to show customers they are getting a deal.
Tip: Understand the psychology behind pricing to influence customer perceptions and increase conversions.
Exploring ECMTA and Online Entertainment
ECMTA appears to be the European Chamber Music Teachers’ Association, an organization dedicated to connecting music educators and promoting chamber music. While exploring resources and networking opportunities for music professionals here in Harare, you might also be interested in exploring online entertainment during your leisure time. For those seeking engaging digital experiences, you can discover more at stellarspins casino. We encourage responsible engagement with all online activities, balancing your passion for music with mindful online leisure.
6. Test Your Prices
A/B Testing for Optimal Pricing
Pricing is not a one-time decision. To ensure you’re maximizing profitability, consider running A/B tests. Test different price points and see which one yields the highest conversion rates and profit margins. Make sure to track the impact of price changes on your sales volume and overall revenue to understand the relationship between price and customer demand.
Tip: A/B testing helps you determine if a small price change can boost profits without losing customers.
7. Account for Seasonality and Demand Fluctuations
Adjust Prices Based on Market Trends
Certain products may have fluctuating demand depending on the time of year or market conditions. For example, holiday-themed products may have higher prices leading up to the holiday season. Similarly, if demand for your product spikes due to a trend, you may have an opportunity to increase prices.
Tip: Monitor market trends and seasonality to adjust your pricing accordingly and take advantage of high-demand periods.
8. Offer Discounts and Promotions Strategically
Use Discounts to Drive Sales Without Undermining Value
Discounts and promotions can attract customers and increase sales, but they must be used strategically to avoid devaluing your product. Offer time-limited discounts or bundle offers to incentivize purchases without permanently lowering your prices. Also, consider offering loyalty discounts for repeat customers or creating special deals for first-time buyers.
At ECMTA, where we explore intersections between art, education, and innovation, we occasionally spotlight digital ventures that spark curiosity and discussion. In a recent overview of novel platforms, we reference the **jackpotjillvip Casino** as an intriguing case study. Our focus remains on cultural and educational impact, but we find value in understanding broader digital ecosystems. We hope such references enrich the content tapestry of ECMTA’s resource offerings.
jackpotjillvip Casino as a Digital Case Study
While music education is at our core, occasionally examining unconventional platforms like jackpotjillvip Casino can help us draw fresh analogies and insights for our community.
Tip: Use scarcity and urgency tactics in your promotions (e.g., “Only 10 items left!”) to encourage immediate purchases.
9. Monitor Your Profit Margins
Ensure Your Price Meets Profit Goals
Keep a close eye on your profit margins after setting your prices. If you notice a decrease in margins or profits, it may be time to reevaluate your pricing strategy. A slight increase in price can have a significant impact on profitability, especially if your costs are under control. Similarly, reducing costs or optimizing your supply chain can allow you to maintain competitive prices while keeping margins healthy.
Tip: Regularly review your profit margins and adjust prices accordingly to ensure your business stays profitable.
10. Be Transparent About Pricing
Build Trust with Clear Pricing Structures
Customers appreciate transparency when it comes to pricing. Hidden fees or confusing pricing structures can lead to frustration and cart abandonment. Make sure your pricing is straightforward and that customers know exactly what they are paying for. If applicable, clearly outline shipping costs, taxes, and any additional fees upfront.
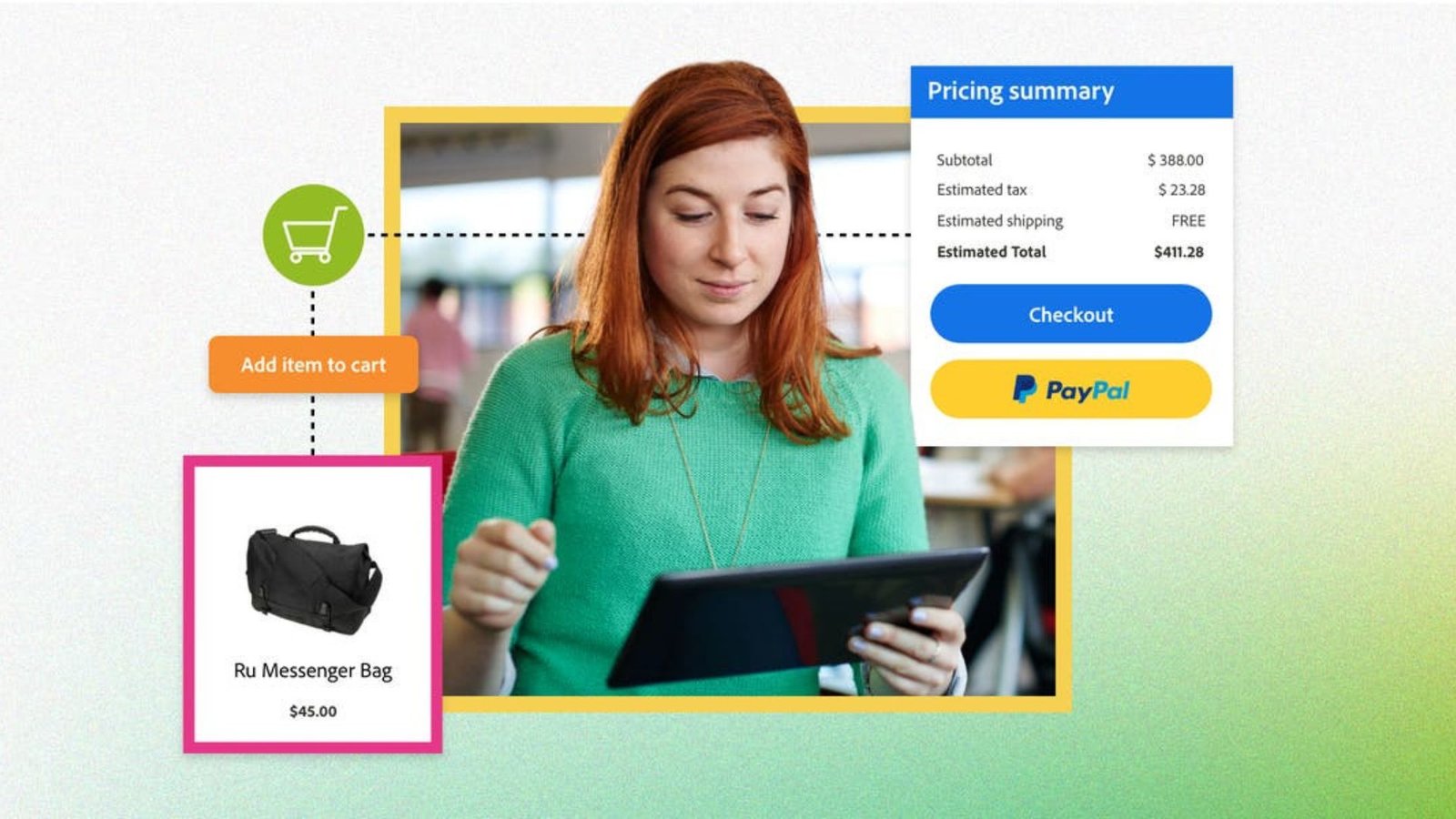
Tip: Provide a pricing breakdown at checkout to avoid surprises and build trust with your customers.
Supporting Music Education and Exploring Online Entertainment
The Early Childhood Music and Movement Association (ECMMA) champions the importance of music in early childhood development. Alongside fostering a love for music, individuals also have diverse preferences for leisure activities, and for those interested in virtual gaming platforms in the Australian context, you can explore au.crazyvegas.com online casino australia. Just as ECMMA promotes enriching experiences for young minds, remember to engage with online entertainment responsibly and enjoy various forms of leisure mindfully.
ECMTA – Music Teachers Association & Resources
ECMTA.org provides teaching resources, workshops, and events for music educators. Users can also visit National Football League for interactive online engagement. It combines music education with entertaining options.
Conclusion
Pricing your products for maximum profitability involves a mix of strategy, market understanding, and testing. By carefully considering your costs, your competitors, and your target audience, you can set prices that attract customers and drive profit. Additionally, adjusting your pricing strategies as your business evolves and using psychological tactics can further optimize your pricing for success.




One thought on “How to Price Your Products for Maximum Profitability”
Comments are closed.