In today’s digital landscape, eCommerce stores are prime targets for cybercriminals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities. From customer data breaches to financial fraud, the risks are significant, making robust cybersecurity measures a necessity for online businesses. This article provides practical strategies to safeguard your eCommerce store against cyber threats.
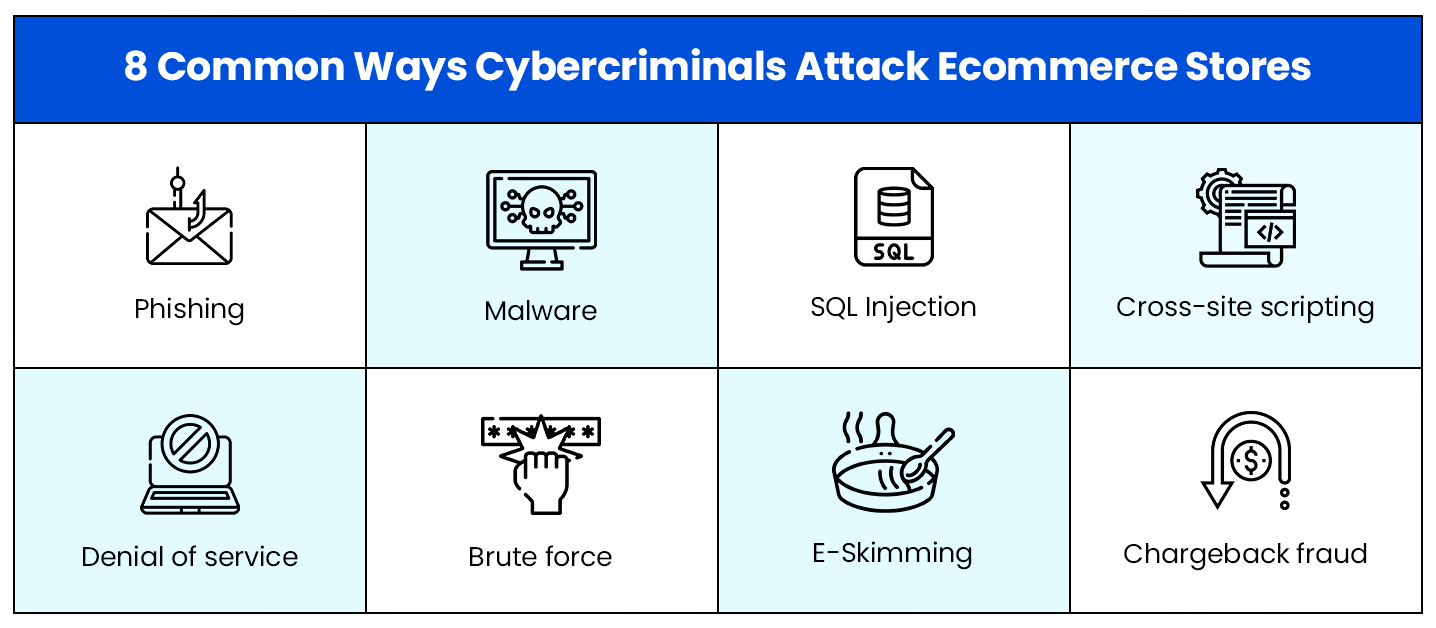
1. Common Cyber Threats Faced by eCommerce Stores
Understanding the risks is the first step to fortifying your eCommerce platform. Some of the most prevalent threats include:
- Phishing Attacks: Fraudulent emails or websites that trick users into revealing sensitive information.
- DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) Attacks: Overwhelming your server with traffic to disrupt services.
- SQL Injections: Exploiting database vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access.
- Ransomware: Locking your data and demanding a ransom for its release.
- Credit Card Fraud: Stealing customer payment details during transactions.
2. Implement Strong Authentication
1. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
Require users to verify their identity through multiple methods, such as a password and a one-time code sent via SMS or email.
2. Strong Password Policies:
Encourage the use of complex passwords and implement regular password updates.
3. Secure Your Website with HTTPS
Using HTTPS ensures that data exchanged between your website and users is encrypted. Obtain an SSL/TLS certificate for your site to build customer trust and comply with security best practices.

4. Regularly Update and Patch Software
Cybercriminals often exploit outdated software. To minimize vulnerabilities:
- Update your eCommerce platform, plugins, and extensions regularly.
- Use automated patch management tools to streamline updates.
5. Protect Customer Payment Information
1. PCI DSS Compliance:
Adhere to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS) to protect customer payment details.
2. Tokenization:
Replace sensitive payment data with unique tokens that cannot be deciphered.
3. Secure Payment Gateways:
Use reputable gateways that offer fraud protection and encryption services.
6. Deploy a Web Application Firewall (WAF)
A WAF monitors and filters incoming traffic to your website, blocking malicious requests and shielding against attacks like SQL injections and cross-site scripting (XSS).
7. Conduct Regular Security Audits
1. Vulnerability Assessments:
Identify weak points in your system through regular scans.
2. Penetration Testing:
Simulate cyberattacks to evaluate your store’s defenses.
3. Security Logs Monitoring:
Track login attempts, data access, and unusual activity to detect threats early.
8. Use Cybersecurity Tools
Invest in tools designed to enhance your security infrastructure, such as:
- Antivirus Software: Protect your server from malware and ransomware.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN): Mitigate DDoS attacks and improve website performance.
- Backup Solutions: Ensure regular backups of your data to recover quickly from an attack.
9. Educate Your Team and Customers
1. Employee Training:
Train employees on cybersecurity best practices, such as recognizing phishing attempts and safeguarding login credentials.
2. Customer Awareness:
Provide tips on secure online practices, like verifying website authenticity and using secure payment methods.
10. Establish a Response Plan
Prepare for potential incidents by creating a response plan:
- Identify key stakeholders and their roles.
- Define steps for containing and mitigating threats.
- Regularly test and update your plan.
11. Partner with Cybersecurity Experts
If in-house expertise is limited, consider hiring a cybersecurity consultant or firm to assess and enhance your eCommerce store’s defenses.
Conclusion
Securing your eCommerce store from cyber threats requires a proactive, multi-layered approach. By implementing strong authentication, encrypting data, updating software, and educating stakeholders, you can build a robust defense against attacks. Investing in security not only protects your business but also fosters trust and loyalty among your customers.